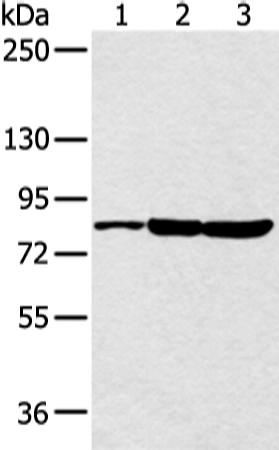
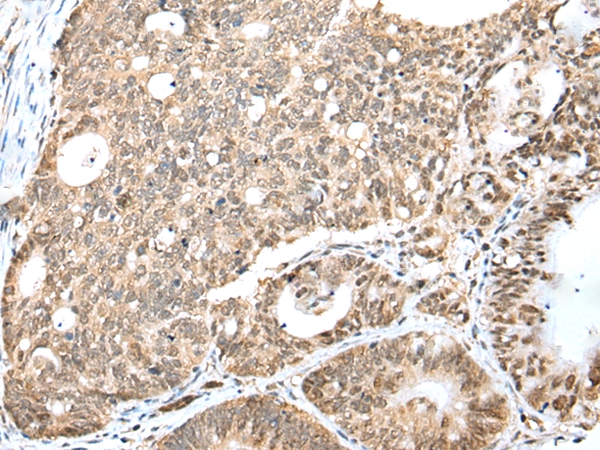
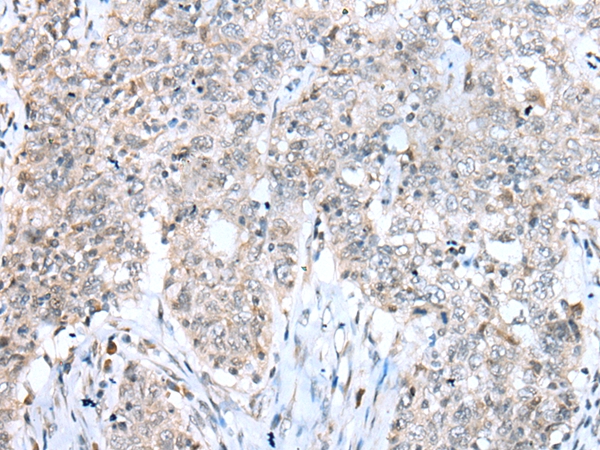
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members are characterized by a dramatic periodicity in protein abundance through the cell cycle. Cyclins function as regulators of CDK kinases. Different cyclins exhibit distinct expression and degradation patterns which contribute to the temporal coordination of each mitotic event. This cyclin and its kinase partner CDK9 were found to be subunits of the transcription elongation factor p-TEFb. The p-TEFb complex containing this cyclin was reported to interact with, and act as a negative regulator of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Tat protein.